In the fast-paced world of cloud computing, availability zones (AZs) play a pivotal role in ensuring the resilience and reliability of cloud services. They are geographically isolated data centres within a cloud region, designed to provide redundancy and fault tolerance.
As the demand for cloud services continues to grow, major cloud providers like Google Cloud, AWS, and Azure have been expanding their global footprint, boasting an impressive number of availability zones worldwide – Google Cloud with 106 zones, AWS with 86 and Azure with 113, and counting at the time of this post.

However, the scenario changes drastically when it comes to small cloud providers, such as ISPs, small DC operators, and hosting providers. They face unique challenges in offering multi availability zone setups, which can significantly impact their ability to compete with larger players in the market.
Why Does a Small Cloud Provider Need Availability Zones?
It’s easy to misinterpret the word ‘small’ and assume that small cloud providers (local, regional, national) will provide their services from a single availability zone alone. However, it is important to note that these providers are ‘small’ only in comparison to the HyperScalers and can enjoy a more concentrated customer footprint in their serviceable region(s). So the reality is quite the contrary as it is these providers who have many more reasons that justify a setup that spans across multiple availability zones.
Also read – VMware Exodus: 5 Reasons Why Apache CloudStack is the Superior Cloud Management Choice
For example:
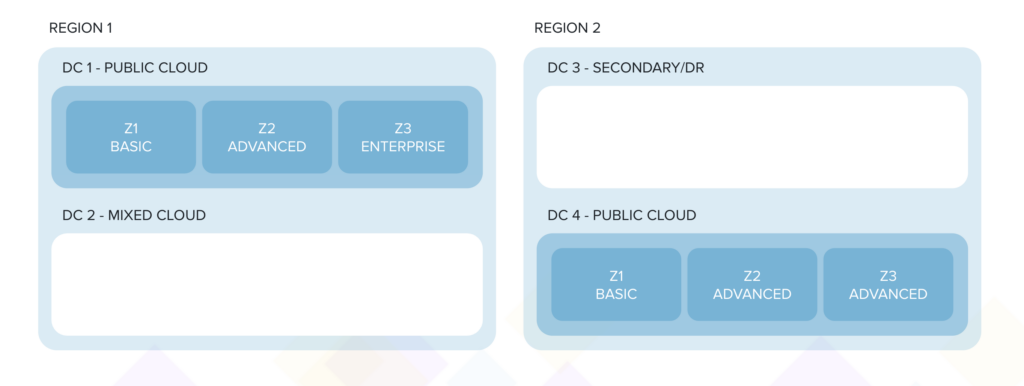
- A regional cloud provider might be offering a public cloud each from 2 co-located data centre regions (DC1 & DC4);
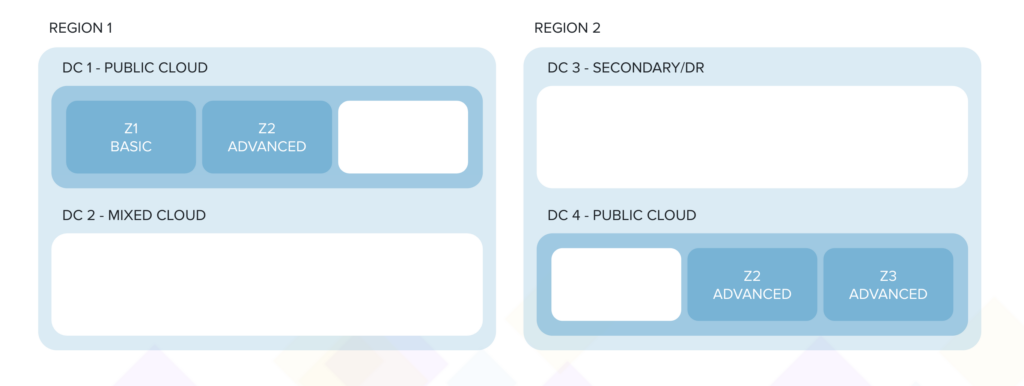
- One or all data centre regions (DC1-Z3) might also contain a zone or a cluster that is dedicated to a segment of customers, e.g., SAP-ready zone for financial enterprises, a zone exclusively dedicated to a distributor etc.;
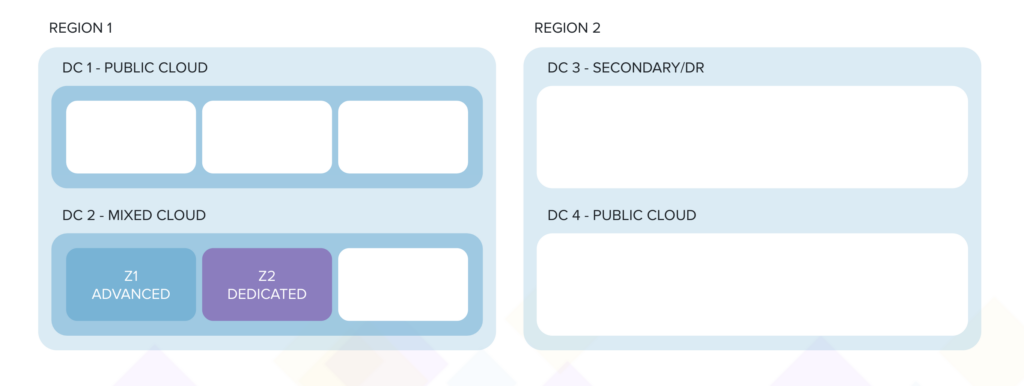
- A ‘mixed’ cloud service that is part public and part dedicated or private (DC2);
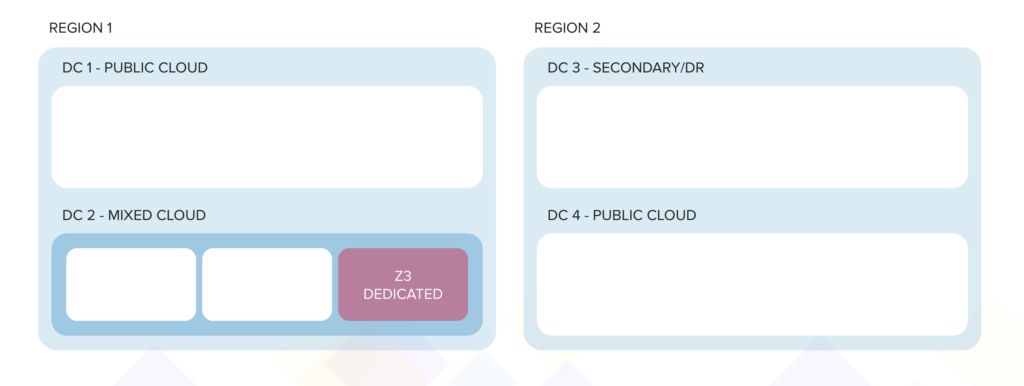
- A wholly dedicated cloud being offered using the same underlying infrastructure for local compliances and government business (DC2-Z3), but with its own independent branding and front fascia.
To simplify and summarise, for smaller cloud providers, the need to expand on their availability footprint is determined not by scale of operations or revenue, but by business requirements around continuity, compliances and brand-led differentiations.
Challenges Arising for Small Cloud Providers
We use Apache CloudStack for workload orchestration. The diagram below, however, is valid for any other orchestrator used for this purpose, as orchestrators, typically, don’t support multiple geographical regions per instance or deployment. Our cloud delivery stack also uses single or multiple CloudStack instances depending on the AZ setup.
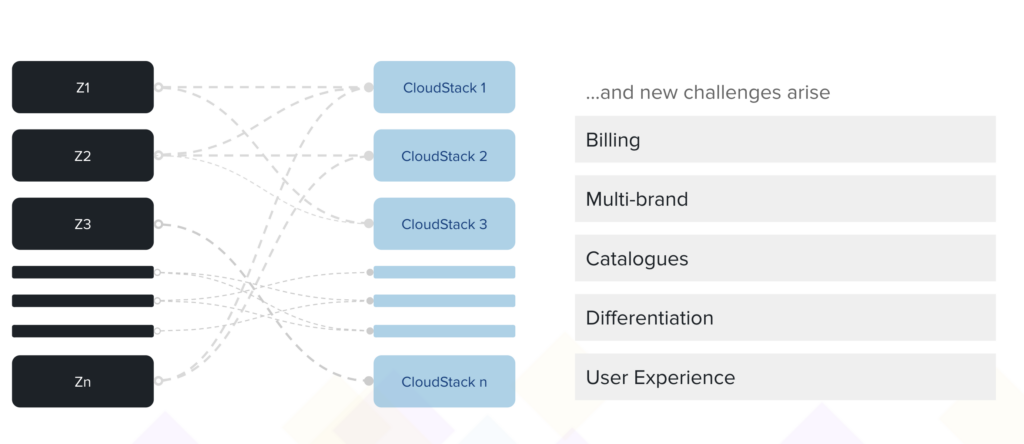
Since all orchestrators were primarily designed to serve an enterprise or a single-tenant use case, a multi-availability zone setup for any cloud provider brings about challenges to achieving:
- Billing across all cloud regions, availability zones and offerings;
- Multi-brand deliveries including own brands and partner brands;
- Customising catalogue availabilities and rules;
- Modern public cloud-like user experience.
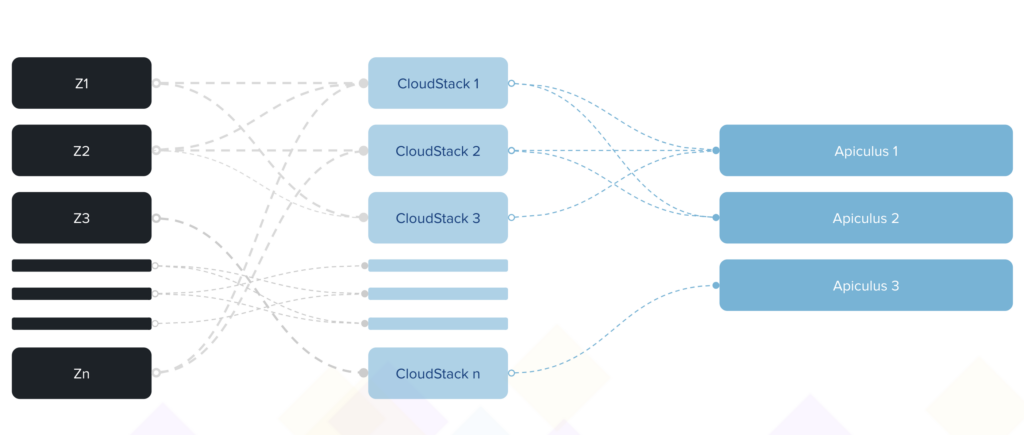
Enter: Apiculus.cloud
This is where Apiculus comes in, as it simply sits atop the CloudStack system and extends its technical and orchestration capabilities to a powerful business administration and management suite.
Also read – Scaling New Heights: Exploring the Latest Advancements in Apache CloudStack
Using Apiculus, cloud providers can set up a multi-availability zone service and offer single-site, multi-site, compliance and other co-branded services using the same infrastructure topology.
And in the process, enjoy the added benefit of making their service footprint appear ‘larger’.
Case Study: Yotta
We implemented such a multi-availability zone structure for Yotta, one of India’s largest data centre provider. The multi-availability zone structure stemmed from Yotta’s requirement to host their own multi-region cloud service, set up a compliance cloud, and also offer cloud-as-a-service to one of their customers – all from their three data centre regions.
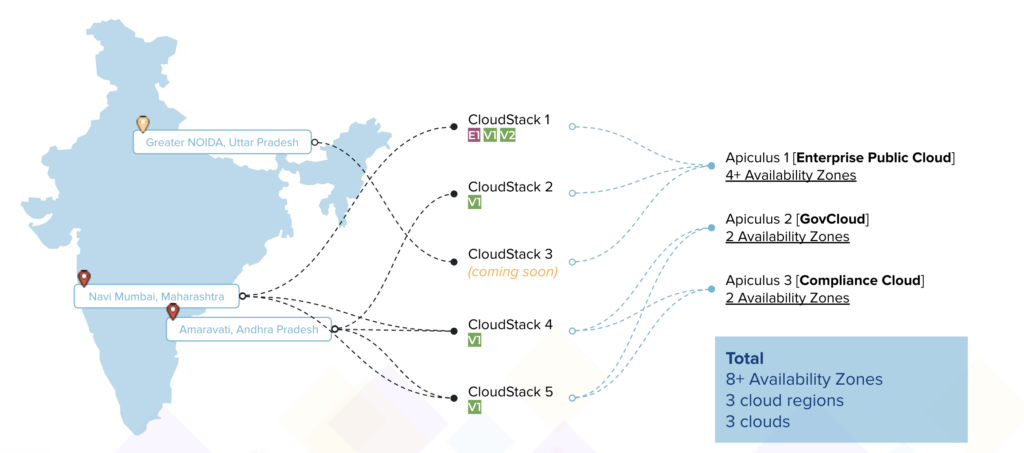
Using CloudStack, Yotta set up the infrastructure management plane in various flavours; and using Apiculus, they were able to set up the front fascia for each of their customer use cases.
Summing it Up
For small cloud providers, implementing cloud with multi-availability zones can be a strategic boost in terms of delivery, branding and GTM.
Also read – CloudStack vs. OpenStack: A Showdown for Simplicity and Speed
With enhanced reliability, improved fault tolerance, and built-in disaster recovery capabilities, multi-availability zone clouds empower cloud providers to deliver top-tier services and support their customers’ growing needs while addressing their own unique use cases around structuring their cloud services.
As the cloud computing landscape continues to evolve, small cloud providers must seize the opportunity to embrace multi-availability zone architectures and create a lasting competitive advantage.

Kshitish is a ‘startup expert’ and has been involved with early stage startups, seeing various phases of growth, for more than 15 years. A specialist in Product Management, User Experience, Technology and Product Growth/Strategy, Kshitish is a seasoned entrepreneur with deep expertise in building enterprise products and horizontal/vertical SaaS. Kshitish did his PG in Product Design from NID, Ahmedabad.

